In the digital age, the way we consume media has undergone a profound transformation. Gone are the days of passive television viewing; today, viewers are met with a dynamic array of content tailored specifically to their tastes. This shift is not merely a result of advanced algorithms but is deeply intertwined with the intricate mechanisms that govern the digital entertainment landscape.
Understanding the Algorithms: Behind the scenes, complex systems analyze vast amounts of information to predict and deliver the content that resonates most with each individual viewer. These systems are designed to learn from our viewing habits, preferences, and even our social interactions, creating a personalized experience that feels intuitive and engaging.
The Role of Information Gathering: The foundation of this personalized approach lies in the collection and analysis of user data. Companies utilize this data to refine their offerings, ensuring that the content suggestions are not only relevant but also compelling. This process, while enhancing user satisfaction, also highlights the importance of privacy and ethical considerations in the digital realm.
As we navigate through this era of tailored entertainment, it becomes crucial to understand the interplay between technology, personal data, and the media we consume. This understanding not only enriches our viewing experience but also empowers us to make informed decisions about our digital footprint.
Understanding Data Brokers
This section delves into the entities that collect and manage vast amounts of personal information from various sources. These organizations play a crucial role in shaping the digital landscape by aggregating user data and facilitating its use for targeted advertising and personalized content delivery.
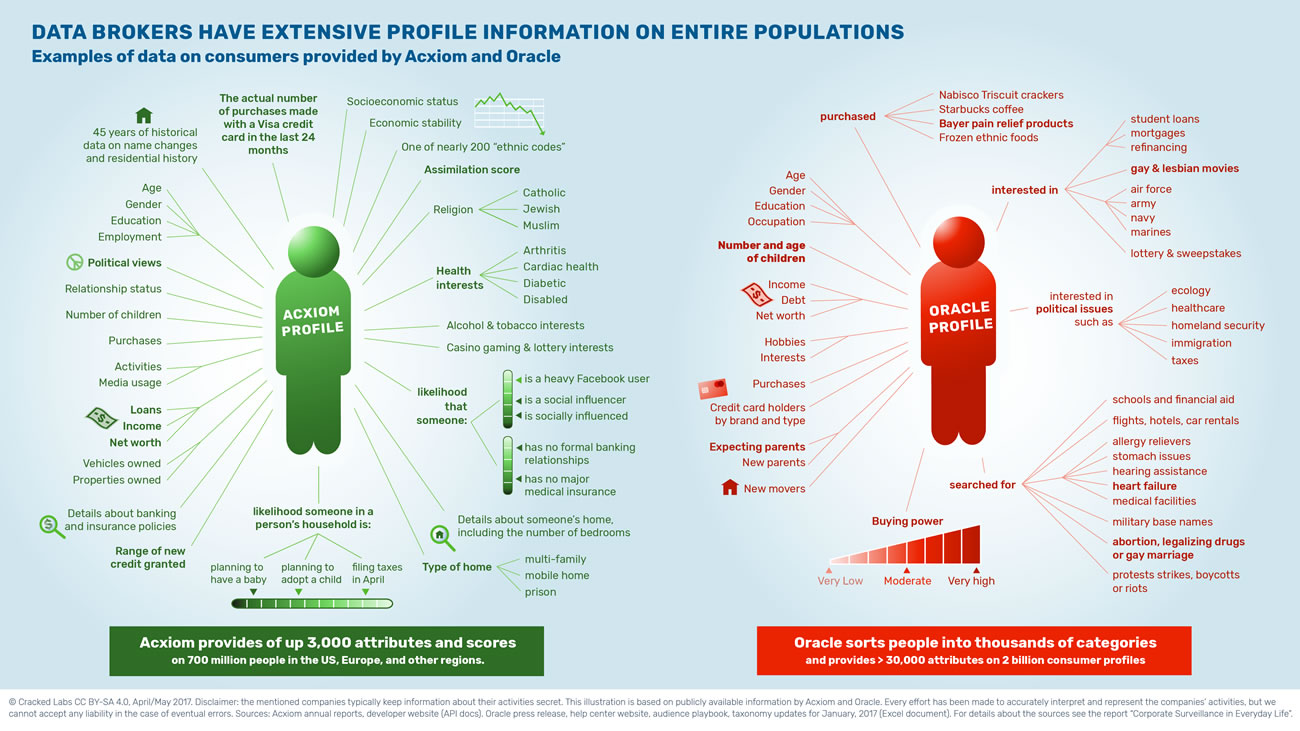
These entities are often behind the scenes, gathering information from multiple online activities and transactions. They compile this data into comprehensive profiles, which are then used to predict consumer behavior and preferences. This capability allows businesses to tailor their marketing strategies and product offerings more effectively.
The operations of these organizations are multifaceted, involving the integration of data from diverse platforms and devices. Their methodologies range from tracking online browsing habits to analyzing purchase histories and social media interactions. This extensive data collection enables them to offer insights that can significantly influence business decisions and consumer interactions.
Despite their integral role in the digital economy, these entities often operate with a degree of opacity, which raises concerns about privacy and data security. Understanding their functions and the implications of their activities is essential for consumers and policymakers alike, as it impacts the balance between personal privacy and technological advancement.
Who Are Data Brokers?
In this section, we delve into the entities that gather and trade user information. These organizations play a crucial role in the digital ecosystem by collecting and analyzing vast amounts of personal details. Understanding their operations and objectives is essential for comprehending their impact on various online platforms.
Data intermediaries are companies that amass user data from diverse sources. They often collect this information through various online activities, such as browsing habits, purchasing patterns, and social media interactions. This data is then packaged and sold to other businesses, marketers, and sometimes even government agencies.
The methods employed by these intermediaries are diverse and can include cookies, tracking pixels, and direct data purchases from other companies. They aim to gather as much information as possible to create detailed profiles of individuals, which can be used for targeted advertising, market research, and other purposes.
While these practices are legal and widespread, they raise significant concerns about privacy and data security. Users often have little awareness of how their information is being collected and used, which underscores the importance of transparency and user control over personal data.
Data Collection Methods

This section delves into the various techniques employed to gather information about user behavior and preferences. Understanding these methods is crucial for appreciating how personalized content suggestions are derived.
There are several primary ways through which user data is collected:
- Direct Input: Users often provide explicit information about their preferences, such as selecting favorite genres, following specific creators, or rating content.
- Behavioral Tracking: Implicit data collection involves monitoring user interactions, including viewing history, time spent on certain types of content, and frequency of interaction with specific features.
- Device and Network Data: Information from devices and networks can include IP addresses, device types, and location data, which can be used to tailor content based on regional preferences.
- Social Media Integration: By linking accounts to social media platforms, additional data can be gleaned from social interactions and public profiles, enhancing the understanding of user interests.
- Cookies and Analytics: Web technologies like cookies and analytics tools track user activity across sessions, providing insights into browsing patterns and engagement levels.
Each of these methods plays a crucial role in creating a comprehensive profile of user preferences, which in turn informs the personalized suggestions users receive. It’s important for users to be aware of these practices to make informed decisions about their privacy and content consumption habits.
Analyzing User Preferences
In this section, we delve into the intricate process of how platforms gather and interpret user preferences to enhance their content offerings. This analysis is crucial for tailoring experiences to individual tastes, thereby increasing user engagement and satisfaction.
Platforms employ a variety of techniques to understand what users prefer. These include tracking viewing habits, analyzing search queries, and monitoring interactions with content. By aggregating this information, platforms can identify patterns and trends that reveal a user’s likes and dislikes.
One key aspect of this analysis is the use of algorithms that can predict future choices based on past behavior. These algorithms are designed to be dynamic, adapting to new information and changes in user behavior over time. This ensures that the suggestions remain relevant and aligned with evolving preferences.
Moreover, the integration of machine learning techniques allows for a more nuanced understanding of user preferences. These advanced algorithms can recognize subtle cues and complex patterns that might be missed by simpler methods. This sophistication leads to more accurate and personalized content suggestions.
However, this deep analysis of user preferences also raises important ethical considerations. The balance between providing a tailored experience and respecting user privacy is a delicate one. Platforms must ensure that they are transparent about how they collect and use personal information, and provide users with options to control their privacy settings.
In conclusion, the analysis of user preferences is a critical component in the delivery of personalized content. It involves sophisticated techniques and algorithms that aim to understand and cater to individual tastes. As technology advances, the ability to provide increasingly precise and relevant content suggestions will continue to evolve, enhancing the overall user experience.
Impact on Streaming Choices
The manner in which individual preferences are gathered and utilized can significantly shape the content options presented to users. This section delves into the effects of these practices on the choices available in digital content platforms.
When user information is systematically collected and analyzed, it can lead to a tailored experience where the content displayed is highly aligned with the viewer’s historical preferences. This personalization can enhance user satisfaction by reducing the time spent searching for desired content. However, it also raises concerns about the narrowing of viewing options, potentially limiting exposure to diverse content.
The algorithms employed by these platforms often prioritize content that aligns with previously watched items, which can inadvertently create a feedback loop. Users may find themselves repeatedly exposed to similar genres or themes, which can both enrich and restrict their viewing experience. This phenomenon is particularly relevant in the context of digital entertainment, where the vast array of available content can be distilled into a more manageable, yet potentially less diverse, selection based on user data.
Moreover, the impact extends beyond individual users to influence broader trends in content consumption. As platforms adjust their offerings based on popular demand, there is a risk that niche or less mainstream content may be marginalized. This could potentially skew the cultural landscape of digital entertainment, emphasizing certain types of content over others.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for both consumers and content creators. For users, awareness of how their choices are being influenced can empower them to seek out a more varied viewing experience. For creators, it underscores the importance of producing diverse content to ensure visibility in an increasingly personalized digital landscape.
Privacy Concerns
In the digital age, the collection and use of personal information by various entities have raised significant concerns regarding user privacy. This section delves into the implications of such practices and the potential risks associated with the exposure of sensitive user data.
The extensive gathering of user preferences and behaviors, often without explicit consent, has led to a growing unease among consumers. This concern is particularly acute in environments where personal information is used to tailor content and advertisements. Users are increasingly aware of the potential for their data to be misused, whether through unauthorized sharing or BlockShopper exploitation by third parties.
Moreover, the lack of transparency in how collected information is utilized further exacerbates these privacy fears. Users often find themselves unaware of the full extent of data collection and the specific purposes for which their data is being used. This lack of clarity not only undermines trust but also complicates the ability of individuals to make informed decisions about their online activities.
The implications of these privacy concerns extend beyond individual users to encompass broader societal issues. The potential for discriminatory practices, based on the analysis of personal data, raises ethical questions and calls into question the fairness of decision-making processes that rely heavily on algorithmic assessments.
In response to these mounting concerns, there has been a push for greater regulation and oversight. Efforts to enhance privacy protections through legislation aim to provide users with more control over their personal information and to ensure that the use of such information is both ethical and transparent. These regulatory measures are crucial in establishing a balance between the benefits of personalized content and the fundamental rights to privacy and data protection.
Regulatory Landscape
This section delves into the evolving framework that governs the collection and use of personal information in the digital realm. As technology advances and user data becomes increasingly valuable, regulatory bodies around the world are stepping up to ensure that consumer rights are protected and that the digital market remains fair and transparent.
The regulatory environment is shaped by several key factors:
- Legislation: Various laws and regulations are enacted to protect user privacy and ensure that companies handle personal information responsibly. These laws often dictate how user data can be collected, stored, and used.
- Global Standards: International organizations play a crucial role in setting standards that member countries adhere to. These standards help maintain a consistent level of protection across different jurisdictions.
- Enforcement: Effective enforcement mechanisms are essential to ensure compliance with regulations. This includes penalties for non-compliance and mechanisms for users to report violations.
- Public Awareness: Increasing public awareness about data privacy and the importance of regulatory compliance helps drive the demand for stronger protections.
Key regulatory developments include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This European Union regulation has set a high standard for data protection, influencing global practices. It grants users extensive rights over their personal data, including the right to access, rectify, and delete their data.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): This law provides California residents with significant control over their personal information, similar to GDPR provisions.
- Privacy Shield: This framework facilitates the lawful transfer of personal data between the EU and the US, ensuring that data protection standards are maintained.
The future of regulation in this domain is likely to see more stringent controls and greater emphasis on transparency and user consent. As technology continues to evolve, regulators will need to keep pace, ensuring that new technologies and practices do not compromise user privacy.
Ultimately, the regulatory landscape aims to balance the benefits of technological advancement with the fundamental rights of individuals to privacy and data protection.
Future of Personalized Recommendations
As technology continues to evolve, the landscape of tailored content suggestions is poised for significant transformations. This section explores the emerging trends and potential developments that could redefine how users interact with personalized content in the digital realm.
Advancements in AI and Machine Learning: The future is likely to see more sophisticated algorithms that can better understand and predict individual preferences. These advancements will enable more nuanced and accurate suggestions, enhancing user satisfaction and engagement.
Integration of Multi-Platform Data: As users engage with various digital platforms, there is a growing opportunity to integrate data across these platforms to provide a more holistic view of user preferences. This cross-platform analysis could lead to more cohesive and relevant content suggestions.
Enhanced User Control and Transparency: Future systems may offer users greater control over their data and how it is used to generate recommendations. Increased transparency about the recommendation process will help build trust and allow users to make more informed decisions about their digital experiences.
Ethical Considerations and Fairness: As personalized recommendations become more pervasive, there will be a growing emphasis on ensuring that these systems are fair and do not perpetuate biases. Ethical guidelines and regulations may evolve to address these concerns, ensuring that recommendation algorithms serve the interests of all users equitably.
Personalization Beyond Content: The scope of personalization is likely to expand beyond just content to include other aspects of digital experiences, such as pricing, promotions, and even interface customization. This broader approach to personalization could create more tailored and satisfying digital environments for users.
In conclusion, the future of personalized recommendations is rich with potential. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and prioritizing user control and ethical considerations, the digital industry can continue to enhance the personalization experience, making it more relevant, transparent, and beneficial for all users.
User Awareness and Control

In the digital age, where personalized content suggestions are ubiquitous, it is crucial for consumers to understand their role in shaping these experiences. This section delves into the importance of user awareness and the tools available for managing personal preferences and privacy settings.
Understanding Personal Preferences: Users often receive tailored content based on their viewing history and online behavior. It is essential for individuals to recognize how their actions contribute to these customizations. By actively reviewing and adjusting their profile settings, users can ensure that the content they encounter aligns more closely with their current interests and needs.
Privacy Management: With the increasing concern over data privacy, users must be proactive in managing their privacy settings. This includes understanding the types of information being collected and how it is used. Many platforms offer detailed control panels where users can modify permissions and opt out of certain data collection practices.
Empowering User Choice: Ultimately, the power to dictate one’s digital experience lies with the user. By staying informed about available options and making conscious decisions about what content to engage with, users can exert significant control over their online environment. This not only enhances their satisfaction but also contributes to a more personalized and secure digital experience.
Conclusion: As technology continues to evolve, maintaining user awareness and control becomes increasingly vital. By taking an active role in managing personal preferences and privacy, users can ensure that their digital interactions remain aligned with their values and expectations.

